Traceability in Manufacturing Best Practice

Why Traceability Matters
- Quality Assurance: Traceability allows for swift identification and isolation of defective products, minimising potential recalls and damage to brand reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as food and pharmaceuticals, are subject to stringent regulations. Traceability ensures adherence to these standards such as pressure for businesses to comply with Net Zero targets including scope 3 emissions is likely to increase as 2030 becomes closer.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Real-time tracking of materials and products enables better decision-making and proactive response to potential disruptions.
- Consumer Safety: In case of product recalls or safety concerns, traceability helps to quickly identify affected products and notify consumers.
Key Elements of a Robust Traceability System
1. Unique Identifiers:
- 1D Barcodes: A widely used method for tagging products with unique identifiers.
- RFID Tags: Radio Frequency Identification tags offer contactless tracking and can store more information than barcodes.
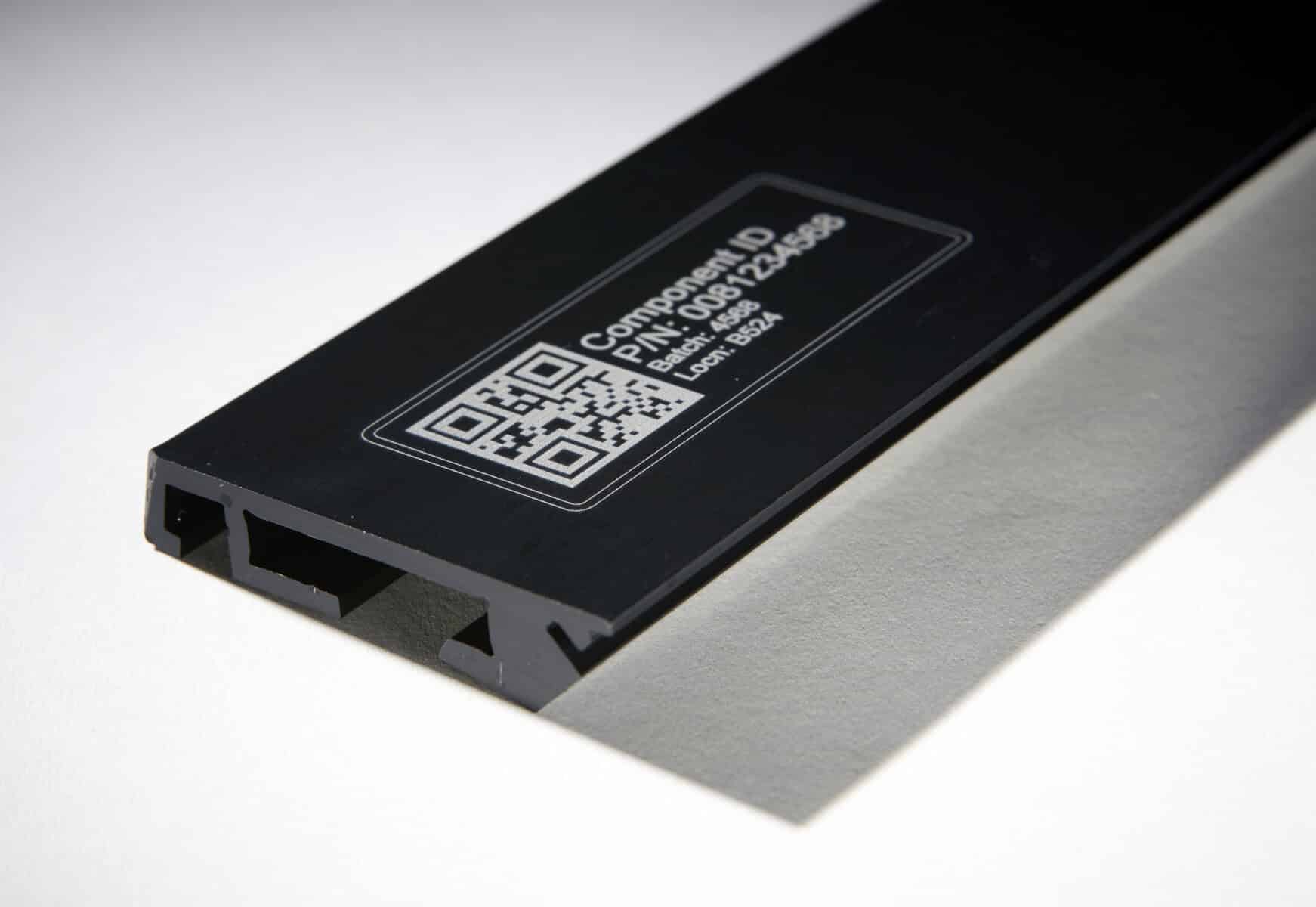
- QR Codes / 2D Barcodes: These two-dimensional barcodes can store a significant amount of data, including product information, manufacturing dates, and lot numbers.
2. Data Capture and Management:
-
-
- Data Collection Devices: Utilise handheld scanners, fixed scanners, or mobile devices to capture data at various stages of the production process.
- Data Management Software: Implement robust software solutions to store, organise, and analyse collected data.
-
3. Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring:
-
-
- IoT (Internet of Things) Integration: Integrate IoT devices to monitor real-time conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and location.
- Sensor Data: Collect sensor data to track product movement and environmental factors.
-
4. Secure Data Storage and Access:
-
-
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Utilise cloud-based platforms to ensure data security and accessibility.
- Data Encryption: Employ strong encryption techniques to protect sensitive information.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit unauthorized access to data.
-
Best Practices for Effective Traceability
-
-
- Standardize Processes: Develop clear and consistent procedures for data collection, entry, and analysis.
- Train Your Team: Ensure that employees are well-trained in using traceability tools and understanding the importance of accurate data entry.
- Validate Data: Implement data validation checks to minimise errors and inconsistencies.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to assess the effectiveness of your traceability system and identify areas for improvement.
- Collaborate with Suppliers: Work closely with suppliers to establish shared traceability standards.
- Stay Updated with Technology: Keep up with the latest advancements in traceability technology to optimise your processes.
- Use Permanent Markings: For traceability to be usable it has to be readable and permanent. Utilise permanent marking techniques rather than processes such as labelling that could become damaged or degraded.
-
Errorproofing and Traceability video explainer
Challenges and Considerations
- Cost: Implementing a comprehensive traceability system can be costly, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. However the cost of implementing a poor process could be even higher in the longer term.
- Complexity: Integrating multiple systems and technologies can be complex and time-consuming.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data is paramount, requiring robust security measures.
- Human Error: Despite technological advancements, human error remains a potential risk.
By carefully considering these challenges and implementing best practices, manufacturers can build robust traceability systems that enhance efficiency, improve quality, and strengthen their overall operations.
Using Laser Engravers and Dot Peen Markers for Traceability
Laser engravers and Dot Peen Markers are two powerful tools for implementing traceability in manufacturing. Laser engraving is a non-contact method that uses a focused laser beam to remove material, creating permanent, high-quality marks. Dot peen marking, on the other hand, is a mechanical process that uses a hardened steel pin, or stylus to indent the surface of a material.
Both methods are versatile and can be used to mark a wide range of materials. In some cases, a combination of the two methods can be used to create a robust traceability system. Key considerations for implementing traceability include mark permanence, readability, data security, and integration with other manufacturing systems.
Conclusion
Traceability is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses operating in today’s competitive and well regulated market. By investing in a well-designed and well-implemented traceability system, manufacturers can gain a significant competitive advantage and build trust with their customers. Talk to Pryor today to see how we can improve your businesses traceability systems.